Sustanability in Chemistry
A natural sieve
Zeolites are aluminium-silicon compounds that are linked by oxygen atoms. This gives them a uniform porous structure that is able to adsorb molecules. These molecular sieves are used to separate and purify gases, and can be regenerated through heating. Zeolites are either naturally extracted or synthetically manufactured. The past few years have seen the Chemistry Division optimize its use of the resources required.
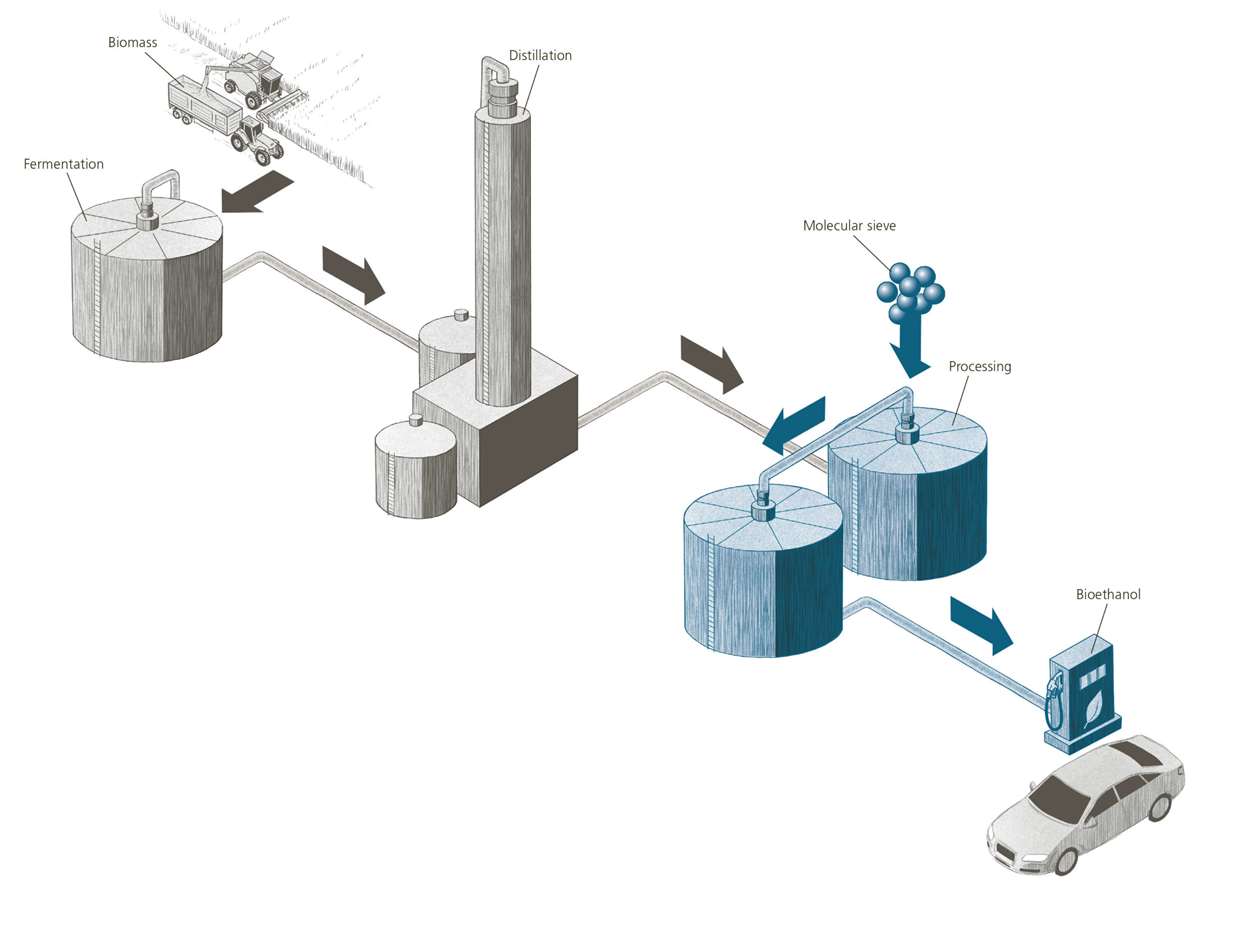
Bioethanol: energy that grows
Bioethanol is an ethyl alcohol that is extracted from biomass and biodegradable waste. As a biological fuel, it is increasingly replacing non-regenerable fossil energy sources. Ethyl alcohol is purified using molecular sieves.
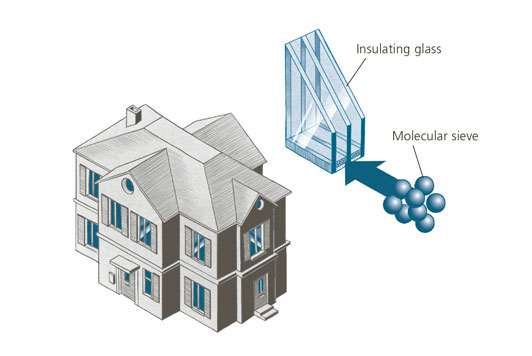
Energy savings through insulating glass
The success of insulating-glass windows is attributable to a large extent to molecular sieves, which adsorb any humidity between the two glass panes to prevent the window from misting. In Germany alone, 17 million simply glazed windows have been replaced with advanced insulating-glass alter- natives, saving 8 000 gigawatt hours of heating energy a year and thereby cutting annual carbon dioxide emissions by some 1.9 million tonnes.
Coal replaced by natural gas
At the division’s production plant in China, acquired in 2016, coal has been replaced as the energy source by the more ecofriendly natural gas. Planning is also under way to provide the plant with a new waste water treatment facility.
Lithium use improved
The division’s US production plant manufactures molecular sieves that are used to concentrate oxygen for medical and industrial applications. The plant has taken a range of actions to improve its utilization of the lithium required in the production process.

Less dust for better air
New filter facilities were installed at the division’s Chinese and US production sites in 2019 to reduce dust emissions and protect employees and the environment alike.

